Functional RNA structures in the 3'UTR of Mosquito-Borne Flaviviruses
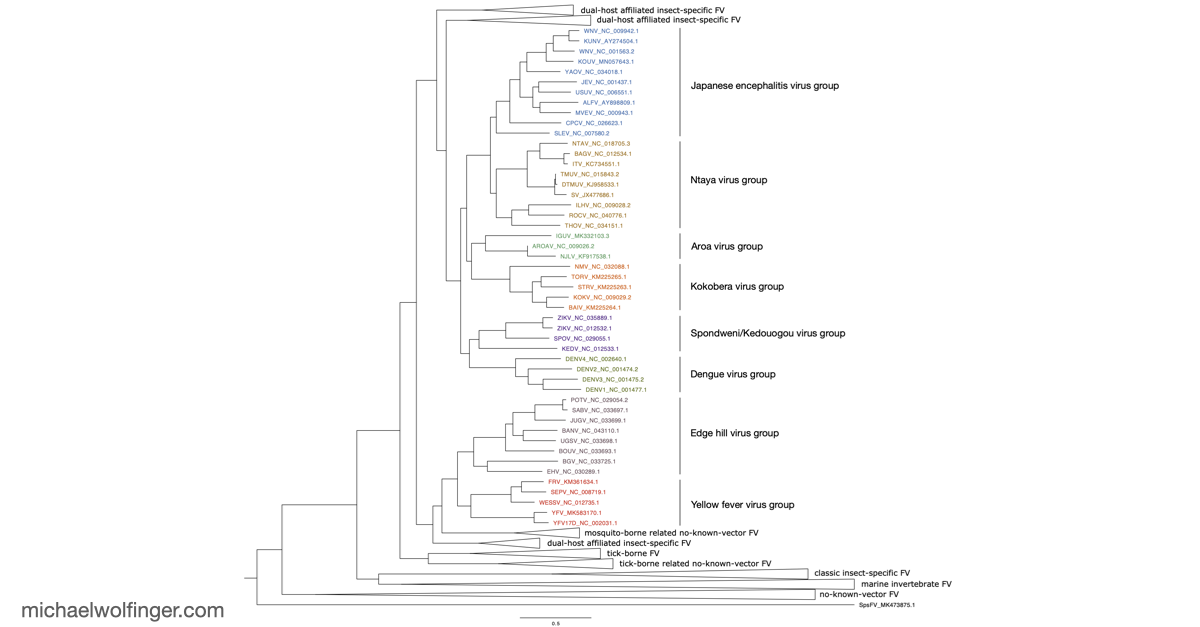
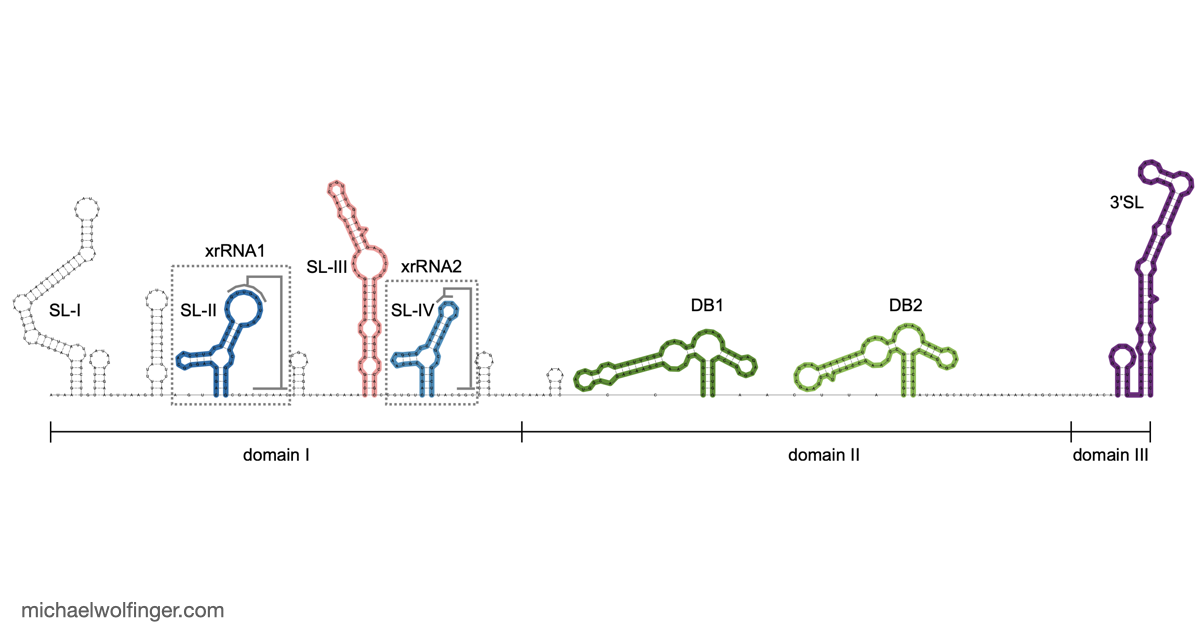
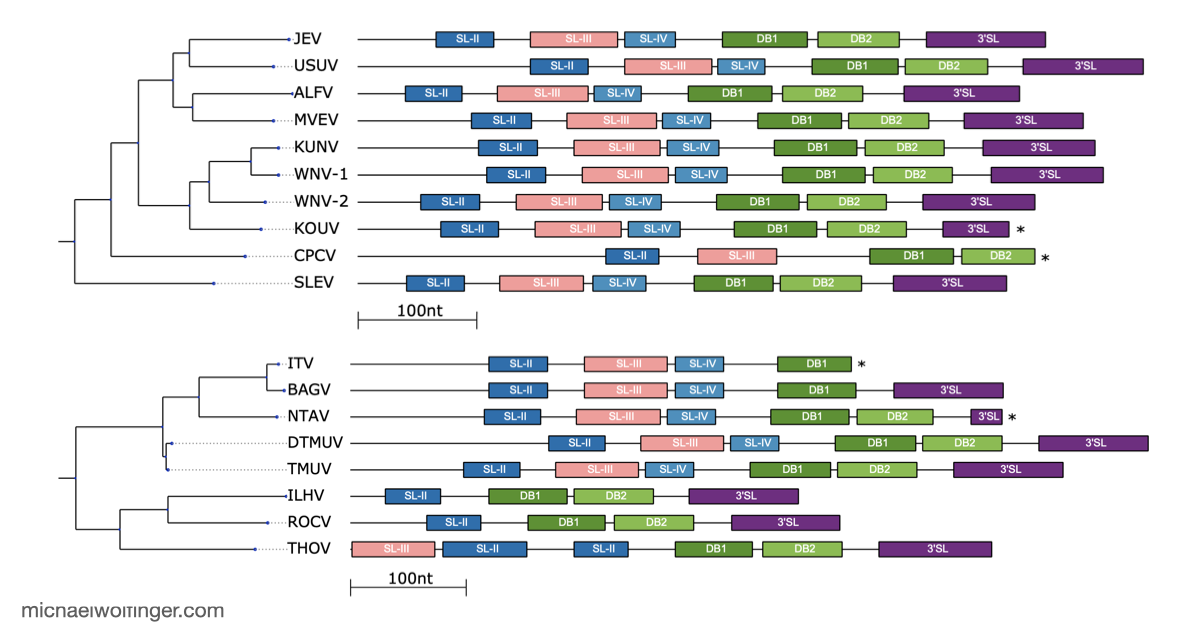
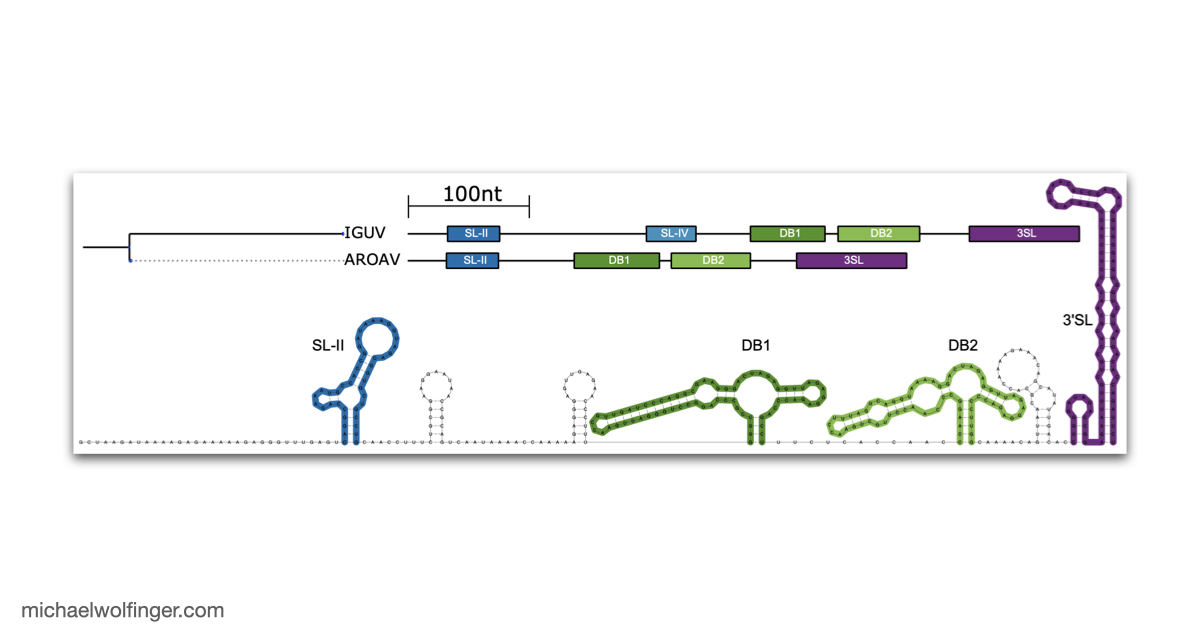
The 3'UTR of Mosquito-Borne Flaviviruses (MBF) contain evolutionarily conserved functional elements, such as exoribonuclease-resistant RNAs (xrRNAs), dumbbell elements or terminal stem-loops. In this contribution we describe, annotate, and compare these elements within different serological groups of MBF
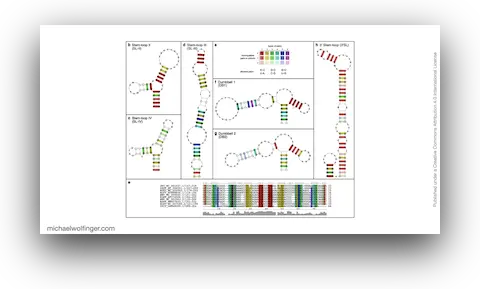
Mosquito-borne flaviviruses (MBF) are responsible for millions of infections in humans and animals each year, posing a significant public health threat. These viruses belong to the Flavivirus family, characterized by their enveloped, non-segmented, single-stranded (+)-sense RNA genome. This genome, known as gRNA, is about 10-12 kilobases long and contains a single open reading frame (ORF) flanked by highly structured untranslated regions (UTRs) at both ends. The UTRs play a crucial role in regulating the viral life cycle by mediating essential processes like genome cyclization, replication, and immune system evasion.
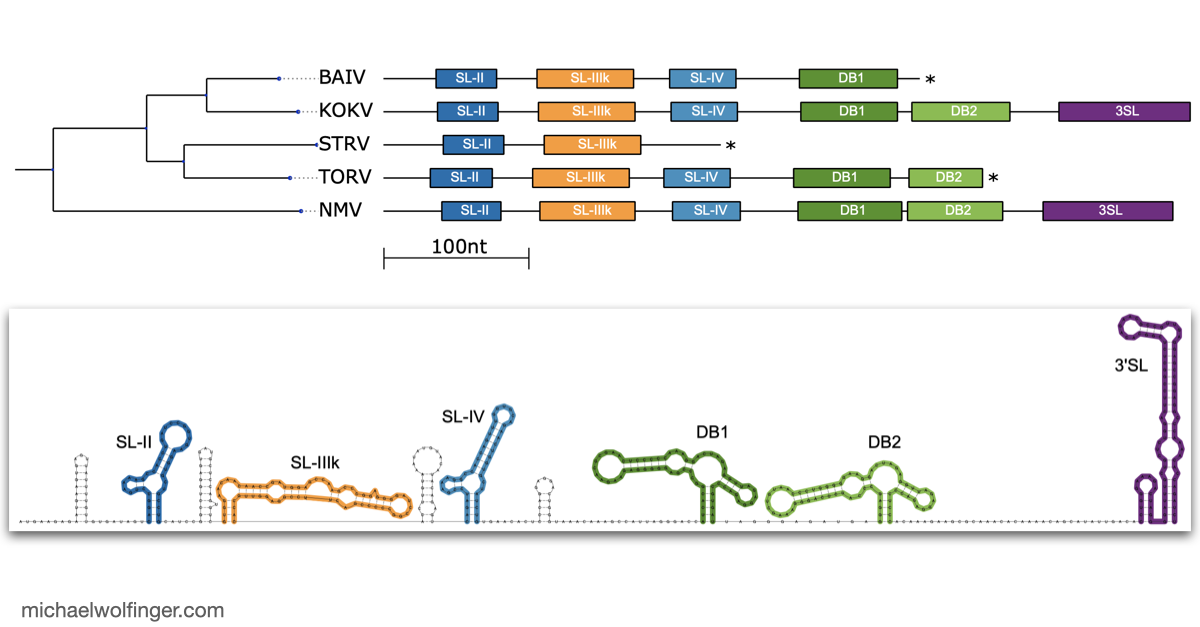
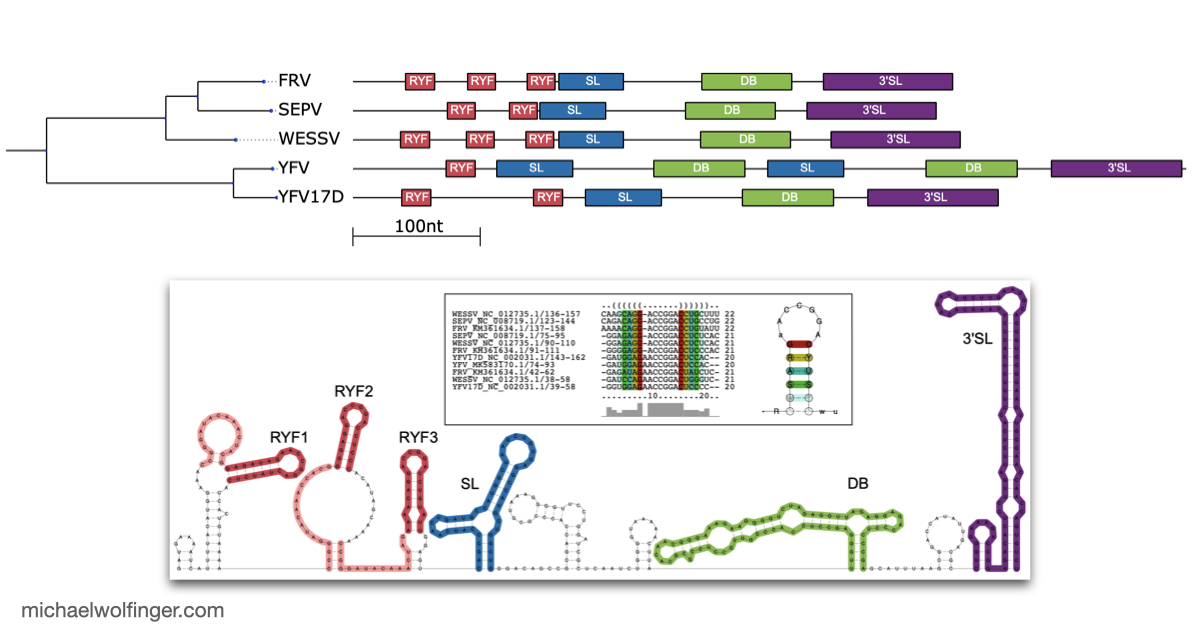
At the heart of these regulatory functions are conserved RNA elements within the flavivirus UTRs. One of the best-studied elements is the exoribonuclease-resistant RNA (xrRNA), which stalls host exoribonucleases like Xrn1. By blocking Xrn1's progression toward the viral 3' end, xrRNAs protect downstream nucleotides from degradation, ensuring the stability of the viral RNA. While xrRNAs are well understood, MBF contain several other conserved RNA structures in their UTRs whose functions remain unknown.
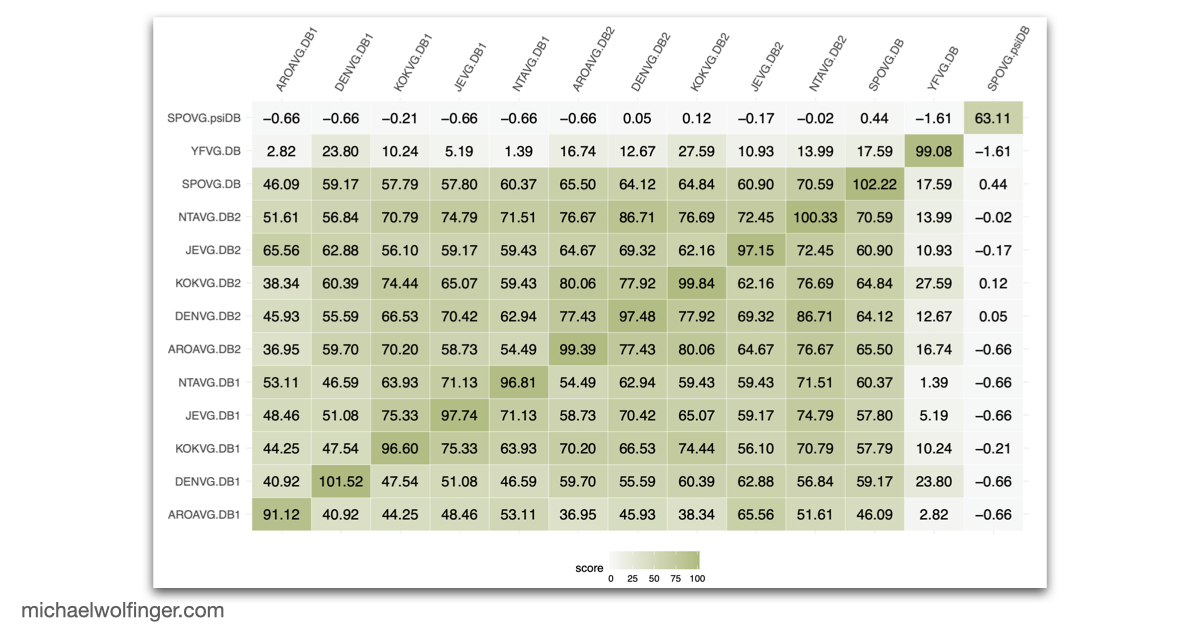
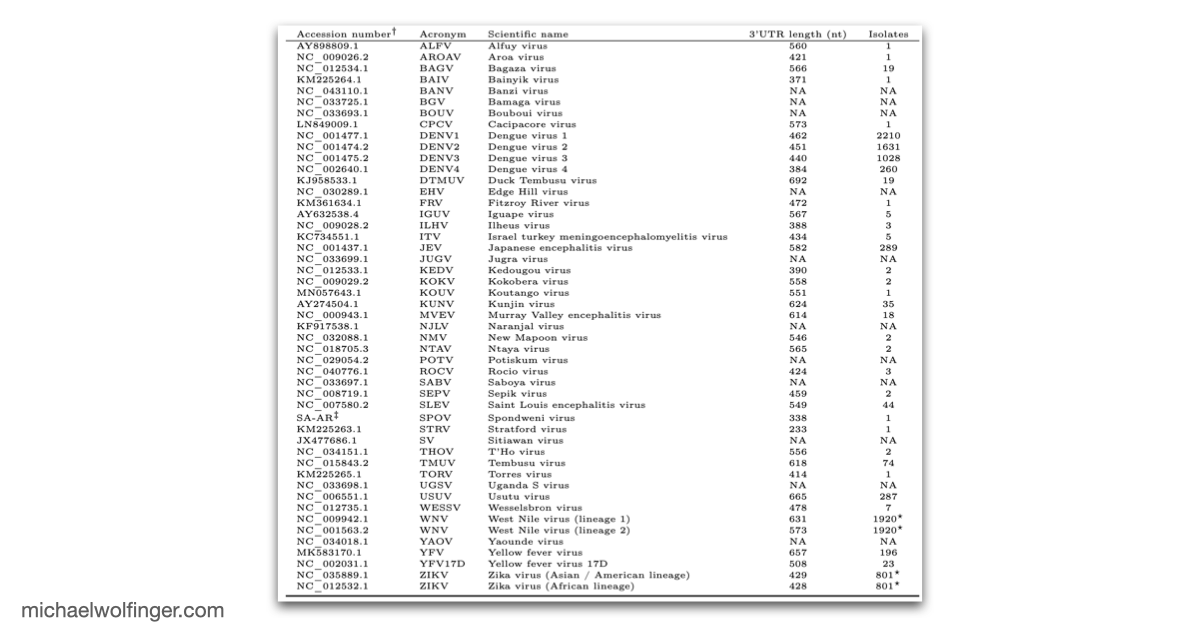
To deepen our understanding of RNA structure conservation in MBF, we recently conducted a comparative genomics screen, focusing on the 3' UTR of all known mosquito-borne flaviviruses. Our findings shed light on the evolutionary pressures that shape these RNA structures and reveal potential new regulatory elements that could be critical to the virus’s survival and pathogenicity.
This research not only expands our knowledge of how flaviviruses manipulate host cells but also opens up new avenues for antiviral strategies targeting these conserved RNA elements.
Figures and Data
Citation
Functional RNA Structures in the 3’UTR of Mosquito-Borne Flaviviruses
Michael T. Wolfinger, Roman Ochsenreiter, Ivo L. Hofacker
In Virus Bioinformatics, edited by Dmitrij Frishman and Manja Marz, pp65–100. Chapman and Hall/CRC Press (2021) | doi: 10.1201/9781003097679-5 | PDF | Figures
See Also
Functional RNA Structures in the 3’UTR of Tick-Borne, Insect-Specific and No Known Vector Flaviviruses
Roman Ochsenreiter, Ivo L. Hofacker, Michael T. Wolfinger
Viruses 11:298 (2019) | doi:10.3390/v11030298 | PDF | Figures
Evolutionary traits of Tick-borne encephalitis virus: Pervasive non-coding RNA structure conservation and molecular epidemiology
Lena S. Kutschera, Michael T. Wolfinger
Virus Evol. (8):1 veac051 (2022) | doi:10.1093/ve/veac051 | PDF | Figures